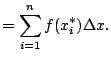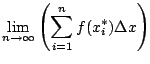Let 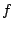 be a continuous function on interval
be a continuous function on interval ![$ [a,b]$](img17.png) .
Divide
.
Divide ![$ [a,b]$](img17.png) into
into 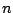 subintervals of length
subintervals of length
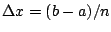 .
Choose (sample) points
.
Choose (sample) points 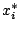 in
in 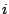 th interval, for each
th interval, for each 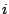 .
The (signed) area between the graph of
.
The (signed) area between the graph of 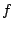 and the
and the 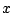 axis is approximately
axis is approximately
(The 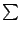 is notation to make it easier to write down and think
about the sum.)
is notation to make it easier to write down and think
about the sum.)
Definition 2.1.1 (Signed Area)
The
(signed) area between the graph of
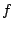
and the
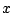
axis between
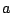
and
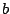
is
(Note that
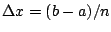
depends on
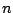
.)
It is a theorem that the area exists and doesn't depend
on the choice of 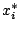 .
.
William Stein
2006-03-15