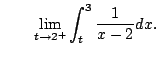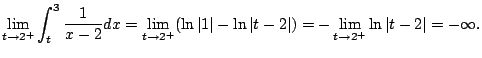Exam 2 Wed Mar 1: 7pm-7:50pm in ??
Today: 7.8 Improper Integrals
Monday - president's day holiday (and almost my bday)
Next -- 11.1 sequences |
Example 5.7.1
Make sense of
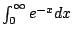
.
The integrals
make sense for each real number
. So consider
Geometrically the area under the whole curve is the limit
of the areas for finite values of
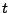
.
Figure 5.7.1:
Graph of 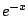
|
|
Example 5.7.2
Consider
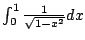
(see Figure
5.7.2).
Figure 5.7.2:
Graph of
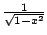
|
|
Problem: The denominator
of the integrand tends to
0 as
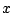
approaches the upper
endpoint.
Define
Here
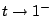
means the limit as
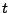
tends to
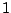 from
the left
from
the left.
Example 5.7.3
There can be multiple points at which the integral is improper.
For example, consider
A crucial point is that we take the limit for the
left and right endpoints independently. We use
the point
0 (for convenience only!) to break
the integral in half.
The graph of
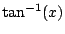
is in Figure
5.7.3.
Figure:
Graph of
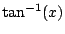
|
|
Example 5.7.4
Brian Conrad's paper on impossibility theorems for elementary
integration begins: ``The Central Limit Theorem in
probability theory assigns a special significance to
the cumulative area function
under the Gaussian bell curve
It is known that
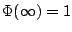
.''
What does this last statement mean? It means that
Example 5.7.5
Consider
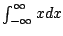
.
Notice that
This diverges since each factor diverges independtly.
But notice that
This is
not what
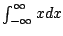
means (in this
course - in a later course it could be interpreted this way)!
This illustrates the importance of treating each bad point
separately (since Example
5.7.3) doesn't.
Example 5.7.6
Consider
![$ \int_{-1}^1 \frac{1}{\sqrt[3]{x}} dx$](img881.png)
.
We have
This illustrates how to be careful and break the function up into two
pieces when there is a discontinuity.
NOTES for 2006-02-22
Midterm 2: Wednesday, March 1, 2006, at 7pm in Pepper Canyon 109
Today: 7.8: Comparison of Improper integrals
11.1: Sequences
Next 11.2 Series
|
Example 5.7.7
Compute
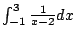
.
A few weeks ago you might have done this:
This is not valid because the function we are
integrating has a pole at
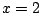
(see Figure
5.7.4).
The integral is improper, and is only defined
if both the following limits exists:
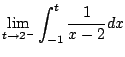
and
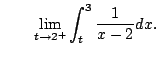
However, the limits diverge, e.g.,
Thus
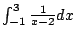
is divergent.
Figure 5.7.4:
Graph of
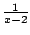
|
|
Subsections
William Stein
2006-03-15
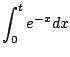
![$\displaystyle \lim_{t\to\infty} \int_0^t e^{-x} dx
= \lim_{t\to\infty} [-e^{-x}]_0^t = 1.
$](img857.png)
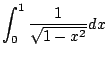
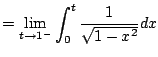
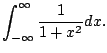
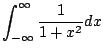
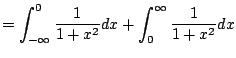
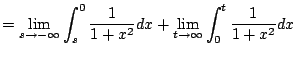
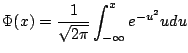
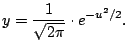
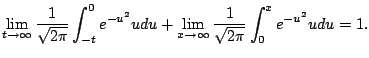
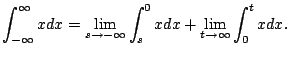
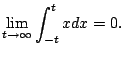
![$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^1 \frac{1}{\sqrt[3]{x}} dx$](img882.png)
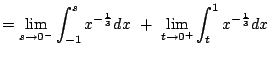
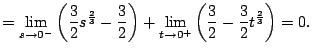
![$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^3 \frac{1}{x-2} dx
= [\ln\vert x-2\vert]_{-1}^{3}
= \ln(3) - \ln(1) \qquad{\text{(totally wrong!)}}
$](img886.png)
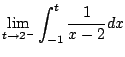 and
and