Next: Polar Coordinates and Complex Up: Applications to Areas, Volume, Previous: Computing Volumes of Surfaces Contents Index
| Quiz Answers: (1) 29, (2)
Exam 1: Wednesday, Feb 1, 7:00pm-7:50pm, here.
Why did we skip from §6.5 to §10.3? Later we'll go back and look at trig functions and complex exponentials; these ideas will fit together more than you might expect. We'll go back to §7.1 on Feb 3. |
In this section we use Riemann sums to extend the familiar notion of an average, which provides yet another physical interpretation of integration.
Recall: Suppose
![]() are the amount of rain each
day in La Jolla, since you moved here. The average rainful
per day is
are the amount of rain each
day in La Jolla, since you moved here. The average rainful
per day is
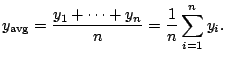
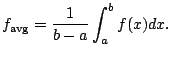
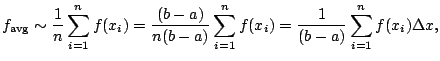
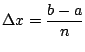 .
This is a Riemann sum!
.
This is a Riemann sum!
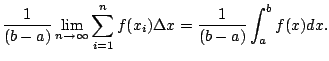
Observation: If you multiply both sides by ![]() in
Definition 3.3.1, you see that the average value times the
length of the interval is the area, i.e., the average value gives you
a rectangle with the same area as the area under your function.
In particular, in Figure 3.3.1 the area between
the
in
Definition 3.3.1, you see that the average value times the
length of the interval is the area, i.e., the average value gives you
a rectangle with the same area as the area under your function.
In particular, in Figure 3.3.1 the area between
the ![]() -axis and
-axis and ![]() is exactly the same as the
area between the horizontal line of height
is exactly the same as the
area between the horizontal line of height ![]() and the
and the ![]() -axis.
-axis.
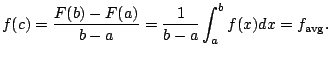
William Stein 2006-03-15